JSON Web Tokens JWT: A Secure Authentication Method
In modern web applications, JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are frequently utilized for user authentication and API security. As a matter of fact, They offer a stateless and secure method of controlling user sessions.
These tokens are self-contained, small, and safe for URLs. They are therefore ideal for scalable and distributed systems. JWTs are particularly helpful in single-page applications (SPAs) and microservices.
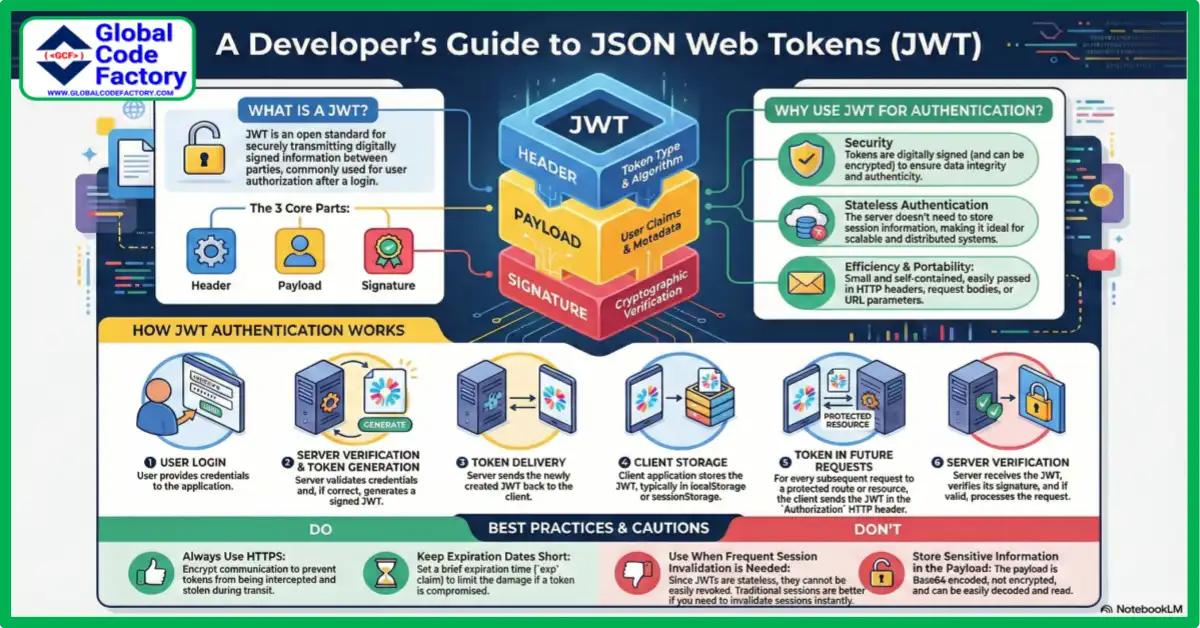
What is JSON Web Tokens (JWT)?
JWT stands for JSON Web Token. It is an open standard for securely transmitting information between parties.
The information has a digital signature. Consequently, it is trustworthy and verifiable. JWTs are often used to authorize users after they log in.
A JWT contains three parts:
- Header – Contains the algorithm and token type.
- Payload – Holds user data and claims.
- Signature – Ensures data integrity and authenticity.
Why Use JWT JSON Web Tokens?
The use of JWT for authentication has numerous advantages.
- Stateless Authentication: Not requires server-side session storage.
- Scalability: Ideal for distributed systems.
- Security: Tokens are having signature and optionally encrypted.
- Efficiency: Tokens are small and can be sent via HTTP headers.
Additionally, JWTs are compatible with a wide range of frameworks and languages. All in all, JWT provides a flexible and scalable solution.
Structure of a JWT
A JWT looks like this:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.
eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.
SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5cDots usage to separate each base64-encoded section.
- The header usually specifies
HS256orRS256algorithm. - The payload includes claims like
sub,name, andexp. - The signature is generated using the secret key and algorithm.
To illustrate, each part has a role: header defines the type, payload carries data, and signature secures the whole.
How JWT JSON Web Tokens Work?
The basic process of JWT authentication is as follows:
- The user enters their credentials to log in.
- Server verifies and generates JWT.
- Delivery of JWT to a client.
- Client stores JWT, typically in localStorage or sessionStorage.
- On future requests, JWT is sent in the HTTP
Authorizationheader - Before responding, the server verifies JWT.
As a result, this process ensures secure access to protected resources.
Implementing JWT in ASP.NET Core
To begin with, Use JWT in ASP.NET Core by doing the following:
1. Install Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer package
2. Configure services in Startup.cs :
3. Afterward, Use authentication middleware in your pipeline:
4. Finally, Create and return a JWT when user logs in.
Best Practices for Using JWT JSON Web Tokens
Use JWT safely and effectively by adhering to following guidelines:
- Always use HTTPS.
- Set brief expiration dates.
- Do not include private information in the payload.
- Use strong secrets or keys.
- Verify tokens for each request.
- Additionally, use refresh tokens for better session control.
With this in mind, JWT usage becomes both practical and secure.
When Not to Use JWT?
JWTs are helpful, but they are not always the best option.
For instance, do not use JWT when:
- When there is need of Frequent invalidation of sessions.
- Tokens must be under server-side control.
- Sensitive information contained in tokens must remain concealed.
In such cases, traditional cookie-based sessions may be more suitable.