Pattern Matching In C#: An Explanation Using Examples
Pattern Matching in C# is a powerful feature introduced in recent versions of C#. Moreover, It enables programmers to produce code that is clearer and more concise.
Logic is readable because to this feature. It makes conditional statements like switch and if simpler. Therefore, This makes it easier to maintain code.
It has improved with each successive version of C#. More power and flexibility have been added with C# 8.0, 9.0, and .NET 6.
Why Use Pattern Matching in C#?
In C#, It aids in avoiding lengthy and disorganized if-else chains. Not only does it provide cleaner syntax, but it also improves performance.
In many cases, developers use it instead of type casting. This approach also helps minimize code duplication.
Pattern matching, for example, makes it possible to simultaneously examine object types and values. This facilitates the understanding of code.
Pattern Matching Types in C#
Let us examine the various pattern matching formats that are offered by current C# versions.
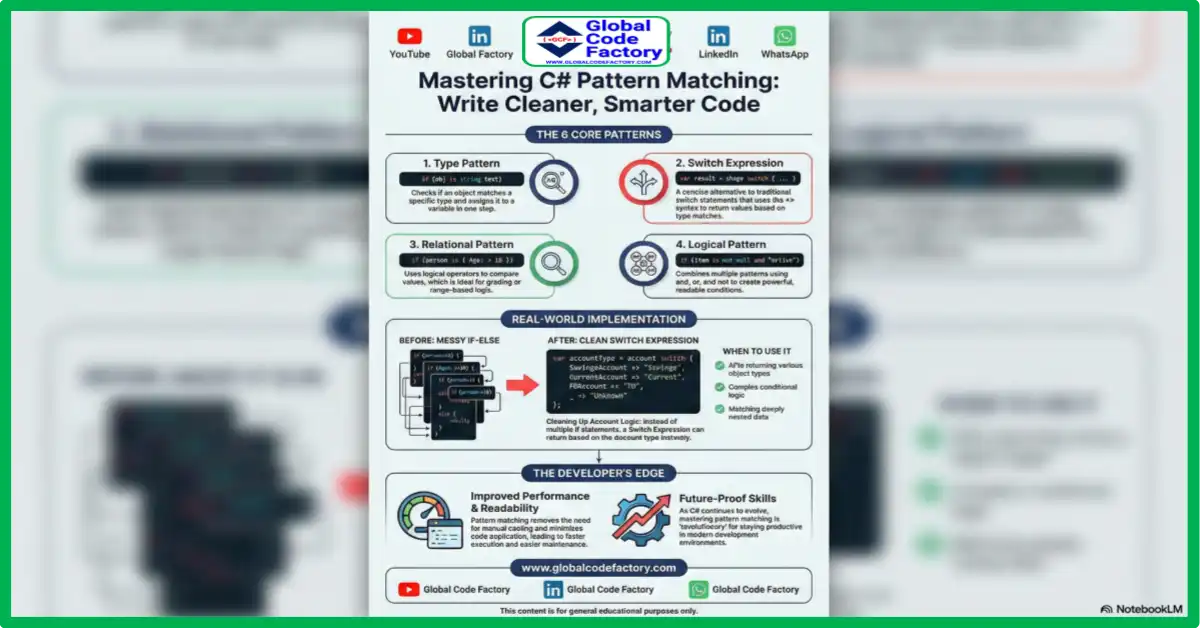
1. Type Pattern
This pattern checks if an object is of a specific type.
Here, obj is tested. If it’s a string, it’s assigned to text.
2. Switch Expression
Switch expressions are a concise alternative to switch statements.
These expressions are easy to read and extend.
3. Relational Pattern
Relational patterns allow comparison using logical operators.
This pattern is especially useful in grading or range-based scenarios.
4. Logical Pattern
You can combine patterns using logical operators like and, or, and not.
This makes your conditions both powerful and readable.
5. Property Pattern
This pattern checks specific properties within objects.
Property patterns are ideal for complex data structures.
6. Positional Pattern
Use this with deconstructed types or tuples.
This is available from C# 9.0 onward.
Real-World Example of Pattern Matching in C#
Benefits of Pattern Matching
- Improves readability
- Minimizes the duplication of code
- Removes needless casting
- Improves performance
- Promotes the use of declarative coding.
Because of these advantages, it is an essential C# feature.
When to Apply Pattern Matching
Make use of it when working with:
- APIs that return a variety of object types.
- Conditional logic that is complex.
- Deconstructed values or tuples.
- Matching deeply nested data structures.
For that reason, pattern matching is perfect for cleaning up switch-heavy logic.